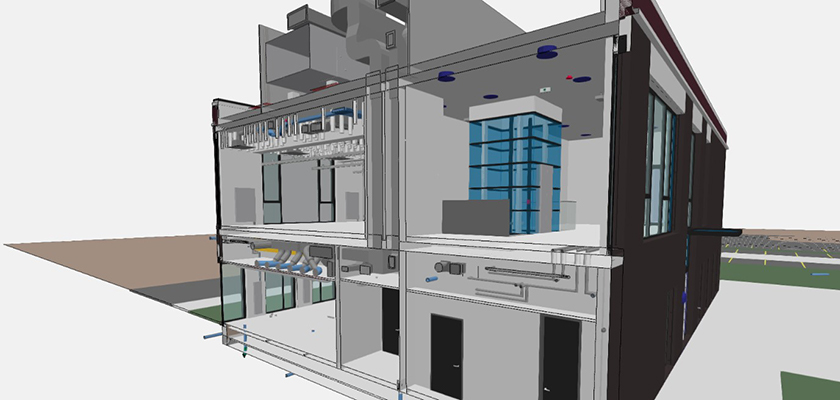
The digitalisation of the construction industry is a process that can no longer be stopped. The BIM snowball is “rolling” through the industry and more and more participants are jumping up. The fast ball is getting bigger and bigger, because those who participate recognize the enormous potentials.
The term BIM Building Information Modelling is used to describe a working method in which project participants perform their work with or on the basis of digital data, a method that is becoming increasingly important. Digital data are usually several geometric 3D models which are attributed with further information, such as material, condition, deadlines and costs, as well as for later operation. Projects should be planned and carried out holistically with BIM from the basic evaluation to completion and subsequent operation.
Perhaps more than anything else, however, BIM is a project management tool that enables project teams to plan with a high degree of accuracy and low collision, to improve communication, to optimize quantity determination, to visualize scheduling, to simulate design activities and to rationalize the operational use of buildings.
At the same time, BIM is a mechanism that supports the management of contracts, assigns tasks and monitors their execution, documents changes, and plans, monitors and documents project progress as a whole.
Ultimately, BIM is also an attitude towards progress and the further development of efficient working methods. Once the decision has been made in favour of BIM in a project, the client and project management must develop an irrevocable attitude towards BIM. “Yes, we can (BIM)”! There will always be doubters, especially in difficult project phases.
As part of project management or separately as BIM consulting, we offer support in the following areas:
General advice on the state of development of the BIM method in Germany, clarification of myths and unfulfillable promises, benefit expenditure
- Needs analysis (Why?) => Motivation
- Setting goals (What?)
- Definition of use cases
- process specifications
- standard defaults
- Description of the procedure (How?)
- Competences (persons/roles)
- Infrastructure (software and hardware, Open BIM)
- Project planning = costs for BIM
Development of company-specific or project-specific BIM strategies
Implementation of strategies in project planning
- Preparation of project BIM specifications (client information requirements AIA)
- Definition of project requirements
- Definition of BIM processes, objectives and applications
Consulting for the selection of a Common Data Environment (CDE)
Development of specific BIM allocation strategies
- Analysis of the performance of potential bidders
- Specifications for pre-contractual preparation of a BIM settlement plan (BAP) by the bidders
Project-accompanying, superordinate BIM management
- Monitoring, quality control of processes and work results
- Participation in BIM coordination talks of planners
- Advising the client on BIM issues
We acquired the qualification for BIM consulting through our training as a BIM professional at the Ruhr University Bochum in 2016. In the meantime, several reference projects with BIM have been implemented as part of project management services. With our support and consulting services, clients have initiated pilot projects and implemented BIM strategies. The integration of BIM and PKMS is currently in the development phase in cooperation with the PKM service provider Conclude.